Topics
- Fractions
- Equivalent Fractions
- Improper Fraction
- Number Line
Description
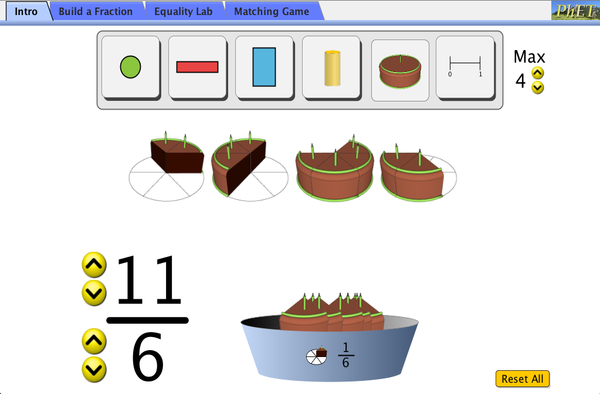
Explore fractions while you help yourself to 1/3 of a chocolate cake and wash it down with 1/2 a glass of water! Create your own fractions using fun interactive objects. Match shapes and numbers to earn stars in the fractions game. Challenge yourself on any level you like. Try to collect lots of stars!
Sample Learning Goals
- Predict and explain how changing the numerator of a fraction affects the fraction's value
- Predict and explain how changing the denominator of a fraction affects the fraction's value
- Convert between a picture of a fraction, a numeric fraction, and a point on a number line
- Build matching fractions using numbers and pictures
- Compare fractions using numbers and patterns
Standards Alignment
Common Core - Math
1.G.A.3
Partition circles and rectangles into two and four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, fourths, and quarters, and use the phrases half of, fourth of, and quarter of. Describe the whole as two of, or four of the shares. Understand for these examples that decomposing into more equal shares creates smaller shares.
2.G.A.2
Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of same-size squares and count to find the total number of them.
2.G.A.3
Partition circles and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc., and describe the whole as two halves, three thirds, four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of identical wholes need not have the same shape.
3.NF.A.1
Understand a fraction 1/b as the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into b equal parts; understand a fraction a/b as the quantity formed by a parts of size 1/b.
3.NF.A.2
Understand a fraction as a number on the number line; represent fractions on a number line diagram.
3.NF.A.2a
Represent a fraction 1/b on a number line diagram by defining the interval from 0 to 1 as the whole and partitioning it into b equal parts. Recognize that each part has size 1/b and that the endpoint of the part based at 0 locates the number 1/b on the number line.
3.NF.A.2b
Represent a fraction a/b on a number line diagram by marking off a lengths 1/b from 0. Recognize that the resulting interval has size a/b and that its endpoint locates the number a/b on the number line.
3.NF.A.3
Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size.
3.NF.A.3a
Understand two fractions as equivalent (equal) if they are the same size, or the same point on a number line.
3.NF.A.3b
Recognize and generate simple equivalent fractions, e.g., 1/2 = 2/4, 4/6 = 2/3. Explain why the fractions are equivalent, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
3.NF.A.3d
Compare two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
Version 1.02